Effects Of Smoking On The Body
Smoking causes pervasive and extensive harm to the body. It harms nearly every organ and leads to various disorders. Tobacco smoke contains toxic chemicals that can expose a smoker to different diseases including cancer, respiratory diseases, and cardiovascular problems.
Understanding these impacts may help smokers appreciate why quitting is so important while adopting healthier lifestyles.
Toxic Chemicals in Tobacco Smoke
| Nicotine | An addictive substance that influences the brain as well as nervous system causing addiction. |
| Tar | gooey fluid that lines the lungs and may cause breathing difficulties as well as cancer. |
| Carbon Monoxide | harmful gas which reduces oxygen supply in tissues or organs thus impairing their functions. |
| Formaldehyde | a poisonous chemical used in building materials such as walls; it can bring about breathing problems associated with cancers. |
| Ammonia | It is often found in cleaning products such respiratory irritantss and damage are caused by it. |
| Hydrogen Cyanide | an extremely poisonous gas that hinders oxygen utilization by body cells leading to serious health consequences. |
| Arsenic | A poisonous element increasing chances of getting cancer or heart diseases with it. |
| Benzene | A known carcinogen responsible for leukemia development cases too among others |
General Health And Cancer Risk
Lung, throat, mouth, esophagus, bladder and pancreas cancers are most common types of cancers caused by exposure to tobacco smoke which contains many carcinogens damaging DNA making repair mechanisms less efficient hence elevate chances for occurrence of malignant tumors significantly among other things.
Smokers also face higher risks of heart disease, stroke, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In general, smokers are not healthy and have shorter lives with increased chances of severe diseases.
Effects on Central Nervous System
Smoking affects both brain functions as well as overall mental health on the central nervous system (CNS).

Brain Function
Nicotine changes the way brain works influencing memory, attention and learning. As a result, smoking for long may lead to cognitive decline and neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer’s disease.
Furthermore, there is a persistent exposure to nicotine which causes structural alterations in specific regions of the brain that regulate mood and emotional balance hence it becomes harder to stop smoking.
Mood And Mental Health
Depression together with anxiety are some of the mental wellness conditions that are directly associated with smoking. Though nicotine could temporarily relieve stress or anxiety, it eventually makes these conditions worse by disrupting normal brain operations.
A person who smokes would more likely suffer from mood swings while those suffering from anxiety or depression will experience an exacerbation of their symptoms due to this habit. Additionally, nicotine withdrawal usually leads to moodiness and irritability.
Vision
Tobacco smoke is made up of chemicals that can damage the optic nerve and reduce blood flow to eyes potentially increasing risk for vision problems. Smokers face higher risks of developing cataracts which make their eye lenses cloudy.
Blindness in the case of elder people is caused by age related macular dystrophy (ARMD) but there is research indicating that this condition takes place much earlier among smokers. A smoker also risks getting dry eye syndrome thereby making his/her eyes dry thus impairing vision.
Neurotransmitter Imbalance
Nicotine affects the neurotransmitters balance in the brain which are mainly concerned with reward and satisfaction. This disruption can lead to addiction, which makes it difficult for someone to quit smoking.
Disturbance of normal neurotransmitter functioning can also influence mood regulation and cause increased irritability, anxiety and trouble focusing. These changes often result in a general decline in mental well-being among smokers.
Increased Risk of Stroke
Smoking is a major cause of stroke because it aids in the accumulation of plaque on arterial walls known as atherosclerosis. Such accumulation may lead to blockage thereby reducing or cutting off blood supply into the brain giving a rise to stroke.
Smokers who have other risk factors like diabetes or high blood pressure are at an even higher risk of having a stroke. Quitting smoking substantially reduces the chances of suffering from a stroke as well as improves overall brain health.
Effects on Respiratory System
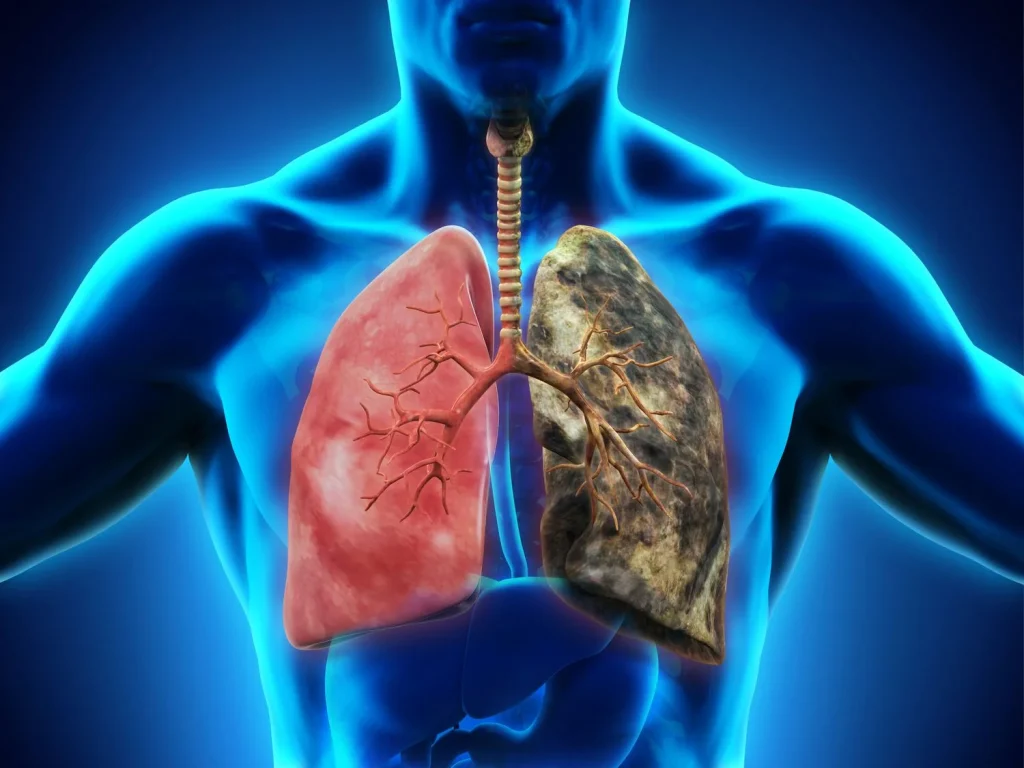
Lung Damage
The lungs are directly affected by inhalation of smoke that causes inflammation and damages airways and lung tissues through tar and other chemicals that come with tobacco products.
This eventually leads to chronic bronchitis, emphysema among other chronic lung diseases. Persistent irritation may also lead to frequent coughs or difficulty breathing.
Cancer Risk
Smoking is mostly responsible for causing lung cancer accounting for about 85% cases. The lungs cells become mutants and start growing cancerously when exposed to carcinogens found in tobacco smoke compounds hence leading cancers development thereupon.
Either more cigarettes consumed per day or longer duration of smoking exposes one to greater risks of developing lung cancer.
Chronic Lung Conditions
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is made up of such lung ailments like chronic bronchitis plus emphysema. They affect breathing making it difficult for sufferers, followed with excessive production mucus i.e, coughing incessantly, thus greatly deteriorating the life quality.
COPD usually progresses and may eventually result in severe respiratory failure.
In Infants, Children, and Teens
Second hand smoke is particularly harmful for babies, children and teens. It is one of the major causes of sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS), respiratory infections, asthma attacks including reduced lung growth.
Children who are frequently exposed to second hand tobacco smoke also tend to become smokers themselves thus continuing chain of health conditions.
Effects on Sexuality and Reproductive System
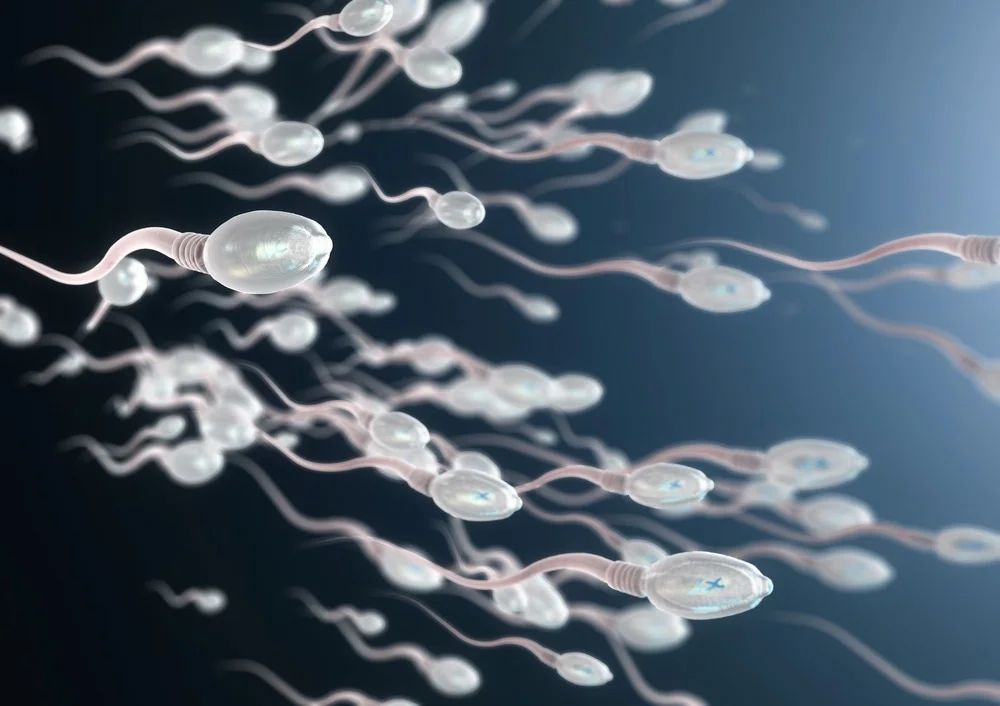
Fertility Problems
Both males and females smoking can lead to fertility problems. It affects hormones production, destroying reproductive organs as well as reducing chances of getting pregnant.
A woman who smokes has higher chances of being infertile than nonsmoking ones and might suffer complications when she becomes pregnant.
In People with Vaginas
Smoking women have decreased fertility rates, greater chances of a miscarriage or pregnancy problems (e.g., preterm labor , low birth weight).
Additionally cigarettes have been recognized as a predisposing factor towards both cervical cancer occurrence as well as menstrual irregularities.
In People with Penises
Impairment in blood flow caused by smoking increases men’s risk for having erectile dysfunction.
Smoking also lowers sperm quality leading to infertility and increasing possibility that offspring born may have genetic defects.
Cardiovascular System
Secondhand Smoke Non-smokers are at more danger of suffering from cardiovascular diseases due to exposure to environmental tobacco smoke that comes from people near them who are smokers.
Through causing a variety of cardiovascular events like stroke or heart attack non-smokers inhaling sids experience an increase in these health risks. Smoke chemicals affect blood vessels causing altered anatomy which leads to atherosclerosis among other cardio vascular inaccuracies.
Integumentary system (Skin, Hair, and Nails)

Skin
Smoking fastens the aging of skin which leads to premature wrinkles, fine lines and sagging. The nicotine-induced reduced blood flow constricts blood vessels thus starving the skin of essential nutrients and oxygen.
This leads to a dull complexion and delayed wound healing. Further exposure to tobacco smoke causes psoriasis in smokers as well as increasing their vulnerability to skin cancer due to its hazardous chemical composition.
Hair
The effects of smoking also extend to hair that becomes dry, fragile, and more easily damaged. Nicotine and other components present in tobacco smoke disorder blood flow around the hair follicles hence weakening hair growth while enhancing loss of hair.
Smokers are more prone to early graying and thinning of hair. Besides that, it makes scalp disorders such as dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis worse.
Nails
Furthermore, nails can be discolored or become brittle from smoking leading them susceptible for fungal infections. Nail health is disturbed by toxins obtained from tobacco smoke making them grow slowly while causing structural harm.
Tar from cigarettes results in yellow or brown stains on a smoker’s nails with nicotine being another cause of nail discoloration among smokers. undernourished by poor circulation caused by smoking that can lead to nail deformities with increased brittleness.
Digestive System

Cancer Risk
Tobacco use increases the chances of getting cancers in various organs within the digestive tract including mouth, throat, esophagus, pancreas, stomach, liver and colon respectively this is because carcinogens are present in these smokes leading to mutations/damage at sites leading into cancerous development.
Type 2 Diabetes
The impact of nicotine on insulin resistance and sugar levels leaves smokers at risk for developing type 2 diabetes.The management of diabetes becomes complicated when patients continue smoking their risks for complications also increases drastically.
Periodontal Disease
Periodontal diseases which affect gums and bones that support teeth are caused by smoking. This is something that can cause gum inflammation, loss of teeth as well as other oral health issues among smokers.
Skeletal System
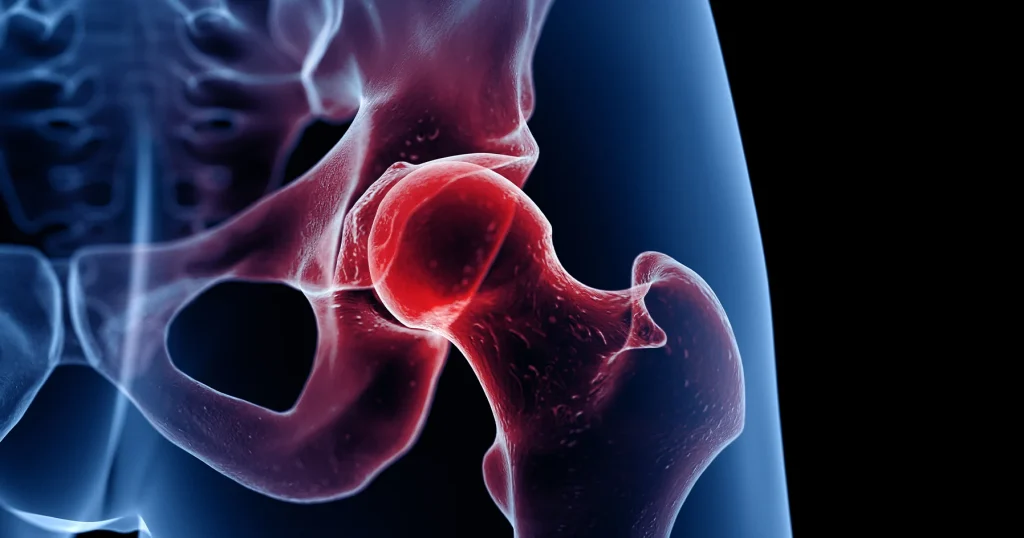
Bone Density
- Smoking reduces bone density increasing probability of osteoporosis.
- Calcium absorption essential for strong bones is interrupted by harmful tobacco chemicals.
- More fragile bones, higher fracture rates in smokers.
Bone Healing
- Nicotine leads to blood vessel constriction thereby reducing blood flow and nutrients supply to the hurt areas.
- Smokers’ healing process in relation to broken bones takes longer compared with people who do not smoke.
- Increased risk of complications, infections and poor surgical results for smokers.
Joint Health
- Smoking increases chances of developing Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), an autoimmune disease that affects joints.
- This is known as joint inflammation leading to pain and damage of the joint thus causing reduced mobility in the affected area called RA disease.
- The symptoms experienced by patients with RA are more severe if they smoke and the disease progresses more rapidly for them than non-smokers who have it too.
Spine Health:
- Degeneration of spinal discs contributes to chronic back pains in smokers due to smoking habit development over time.
- Lessened blood supply damages discus situated at the spine’s position while exposing backbone to rupture occurrence possibilities which happens when a section protrudes from its natural place into another.
- Smokers have increased chances of requiring surgery for spinal related issues.
Overall Skeletal Weakness:
- The overall skeletal system is weakened by the poisonous effects of smoking.
- Bone injuries are common among smokers and their skeletal trauma takes a long time to heal.
- Long-term smoking diminishes general bone strength and firmness of the entire body.
Concluding
Smoking has adverse and comprehensive effects on the body that affect almost all its organ systems. This ranges from a heightened risk of cancer to respiratory and cardiovascular harm among other smoking implications. It is possible for cessation of smoking to lead to substantial health improvements.
Therefore, understanding these consequences will enable individuals to get motivated so as to seek help, or make strides towards a smoke-free life. Remember when thinking about quitting it should be remembered that it is never too late to stop tobacco use and start reaping the benefits of a healthier lifestyle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the immediate benefits of quitting smoking?
Within hours after one stops smoking, their heart rate and blood pressure levels change back into normalcy; in addition there will be carbon monoxide level reduction within few days as well as increase in lung function.
How does smoking affect mental health?
As nicotine addiction sets in depressive symptoms may follow as interrelated anxiety disorders arise in response to withdrawal.
Can smoking-related damage be reversed?
After somebody quits some damages can partially reverse such as improved lung functioning and reduced cardiovascular disease risks but some like those associated with cancer remain elevated.
What resources are available to help quit smoking?
These include things like nicotine replacement therapy (NRT), prescription drugs, counseling, support groups, cessation programs etc.
How does secondhand smoke affect non-smokers?
Non-smokers inhaling secondhand smoke have an increased risk for heart disease, respiratory infections, and cancer especially among children or women who are pregnant.

Russell F. Jones, holding a Master in psychology from the University of Florida. He writes for Smart Parent Solutions, offering practical advice on parenting and child development. His engaging content helps parents navigate family life with confidence and ease. Russell enjoys sharing his knowledge and spending quality time with his family.
