Parents should be concerned if coughing begins in children, however, this should be managed through guidance and proper care. Non-productive coughs, also known as dry coughs, as well as productive coughs, which generate mucus or phlegm, are customary forms of cough. Differentiating between the two, however, is critical in establishing the underlying nature and appropriate management for both conditions.
This article will examine the differences between dry and wet coughs, their causes, the signs and course of treatment for wet coughs, which are typically associated with a significant production of mucus or phlegm. Many families will find this guide particularly useful in helping them understand the various causes of wet coughs in their children and, therefore, be able to deal with them effectively.
What is a dry cough?
As the name dry cough indicates, there is a sensation in the throat accompanied with mucous or phlegm in a cough. This is the usual response of the body when infection occurs and is often attributed to mucous membranes of the throat, nose, and mouth as a lingering cough.
Coughs of this nature often develop during viral illnesses, such as colds or flu and may also be triggered by pollutants in the environment such as smoke, pollution, dirt, or contact with certain plants. Such a cough may also be frequent with the presence of asthma or allergies that further inflame the airways.
What is a Wet Cough?
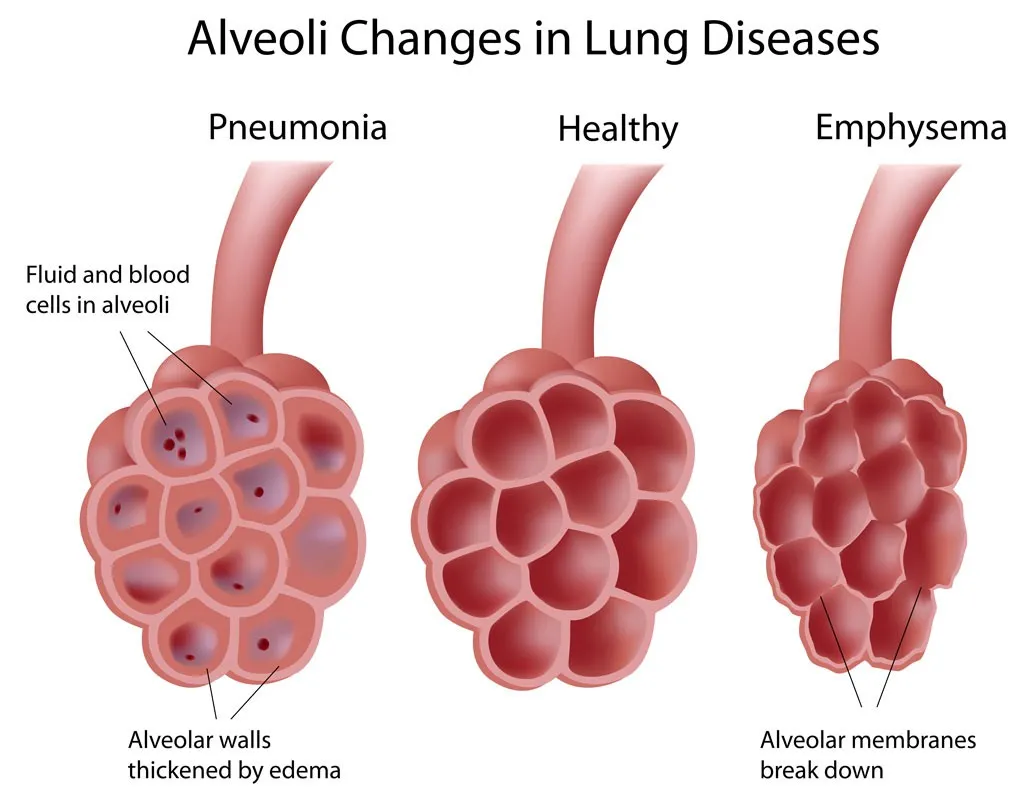
A wet cough, also referred to as a productive cough, is associated with the expulsion of mucus or phlegm. This kind of a cough is prevalent when the respiratory tract is inflamed and affected due to the infection because of mucus formations like in bronchitis or pneumonia.
Other sources of a wet cough can be attributed to post nasal drip where mucus drips from the throat. The sounds produced by a wet cough are different and are referred to as rattling, gurgling, and can exist in abundance and more than a dry cough.

Causes of Dry Cough in Kids
There are several reported reasons behind the occurrence of a dry cough in children which include:
- Viral Infections: Common rounds of cold and flus are known irritants to the throat and as such lead to the onset of a dry cough.
- Environmental Irritants: Occasional exposure to dust, smoke, dry air and other kinds of irritant pollutants can also act as triggers to a dry cough.
- Asthma: In this condition, the airways become swollen and are affected from asthma too much and this leads to dry cough.
- Allergies: Diseases surrounding allergies such as pollen, pet dander or even mold formations can be common allergic reactions and this leads to the development of dry cough.
- Acid Reflux: Other reasons behind a dry cough that can be observed in many cases include the tube present in the throat being able to cause discomfort because of stomach acid and this is mostly more prominent at night.
Causes of Wet Cough in Kids
Not all the causes of a wet cough are the same, in kids there are specific reasons.
- Respiratory Insufficiency: Development of chronic cough due to over production of mucus, like in the case of bronchitis or pneumonia, leads to kids with weak noses experiencing a wet cough.
- Post Nasal Drip: A wet cough may be caused by mucus that moves from the nose to the throat due to an allergy, or as in this case, sinus infection.
- Bacterial Infections: Mucus can be produced when there is a community of bacterial infection in the lungs, accompanied by a productive cough.
- Chronic Lung Conditions: Persistent wet cough may arise from disorders such as cystic fibrosis.
How to Recognize a Dry Cough
- Mucus Absence: No sputum or phlegm is produced from a dry cough.
- Wrinkling: It is possible for children to experience tickle or irritation feeling in the throat.
- Natural Progression: Dry coughs are aggravated by mechanical factors that include dry air or the lateral position of the body.
- Sore or Scratchy Throat: Recurrent continuous cough may give rise to sore or scratchy throat.
- Throat Hoarseness: Enough persistent dry coughing may lead to quaver-increased hoarseness of voice.
How to Recognize a Wet Cough
- Mucus production: The sputum or Phlegm is ejected out with a certain colour such as clear, yellow or green.
- Rattle: A hallmark feature of a wet cough is that it is often accompanied by a gurgle or rattle outward sound because of Mucus being present in the air passage.
- Congested Chest: The child can feel congested or heaviness in the other area of the body such as thorax.
- Breathing difficulty: Even at rest or if the child is supine, there is evidence of straining for breathing pattern.
- Cough duration: A wet cough lasts longer than normal, wet cough lasts even longer in the cases of chronic illness or infections.
How Long Does A Dry Cough Last?
The duration of dry coughs can vary from one case to the other. A cough which can be termed as dry cough in case of a viral illness can last approximately one to two weeks in the instance that other symptoms of the viral infection; for example, sore throats or runny nose, have already gone away.
In circumstances where a dry cough is the result of cough irritants, the cough will often get better once exposure to the irritant is no longer present. However, if asthma or allergy induced dry cough is diagnosed, then such patients are likely to experience chronic dry cough requiring management over an extended period of time.
How Long Does A Wet Cough Last?
Wet coughs caused by chest infections like bronchitis and pneumonia are likely to last longer than the dry cough. These categories of infections may take several weeks to resolve and thus the associated cough may be present even after the other symptoms are gone. In some cases, the presence of nasal drip from sinus infections or allergies can lead to persistent wet cough, and will only respond to treatment for the underlying cause of those infections.
It is advisable to track the course of a cough as well as the amount of time the cough persists so that a doctor may be seen if the condition persists beyond two weeks.
Complications of a Dry Cough Left Untreated
There is a risk of developing several complications if a dry cough is not treated. Irrepressible throat dryness may conclude in various voices being squeaky. In the worst cases, the excessive coughing may disturb sleep and cause a child to be irritated and exhausted.
The child is likely to develop a dry cough if this is directly caused by asthma or allergies, which may result in the development of more serious respiratory problems in subsequent years if not treated appropriately.
Complications of a Wet Cough That Is Not Treated
If the secondary features of a wet cough are not treated, the condition may worsen and increase the risk of developing severe health-related issues, such as pneumonia vague viral illness. In such cases, the infecting pathogen can progress to the lungs or other potential areas of the respiratory tract, leading to pleuritis or even lung cysts.
Very lasting wet coughs may start to develop problems with uncontrollable coughing, painful breath, and unfairly premium fluttering or even high pressure at the chests, which all prompt these underlying conditions to be treated as rapidly as possible.
Management of Dry Cough in Children – Kids from Dry Cough Relief
The typical approach used when managing dry cough is to focus on reducing irritation of the throat and inflammation. Cough syrups containing honey (for children over one year old) or throat lozenges may help soothe the irritation. Keeping the child hydrated with warm liquids like water or herbal tea should also aid in relieving discomfort.
For cases where the child suffe3rs from a chronic dry cough due to asthma or allergies, antihistamines or bronchodilators can be used for one or two weeks to controll the condition.
Management of Wet Cough in Children
In most cases of cough, the source of the sore throat or its causative condition would also be treated. For example, if there is a growth of harmful bacteria trying to induce a cough, then a course of antibiotics will treat the infection as well as reduce mucus production. Viral infections on the other hand may allow the doctors to offer advice meant to speed up recovery such as sufficient rest, liquids, use of humidifier to loosen mucus.
Children can also be given decongestants and expectorants which help them cough up mucus and clear mucus filled airways respectively.
Coughing with throat Comfort at Home
For the management of dry cough over-the-counter product may not be necessary. A child suffering from post-viral cough may benefit from warm fluids such as honey in warm water or herbal tea in the form of throat cache. Moist air can also relieve a child’s dry cough, and using a cool-mist humidifier in the child’s room keeps the air constantly moist so that the cough does not get worse while the child sleeps.
Avoiding smoke and other irritants of the environment is also an important point for dry cough management. Parents can also consider propping a child’s head up so that he or she does not cough as frequently while sleeping.

Coughing with Mucus Releasing Agent at Home
To treat wet cough, home medication concentrates on the removal of the child’s mucus that is preferably thick in consistency. Taking steam bath after a hot shower can successfully loosen the mucus in the chest so that it can be easier for the child to cough it out. The child can also be instructed to take in fluids to hydrate effectively enough to thin the mucus for improved drainage.
Other than these Client draining techniques, keeping a humifier in the room and light percussion to the chest such as gentle pats to the back can also help clear the airways.
When to Consult a Physician in Dry and Wet Coughs
Though many children cough for relatively benign reasons, there will be times that warrant intervention. In cases where a dry cough does not resolve after two weeks, or when it is associated with wheeze, breathlessness, or chest pain, there is a need to visit a doctor. As for other cases, wet coughs lasting above two weeks, producing bloodstained mucus, or leading to breathlessness should seek a doctor’s intervention.
There are other case scenarios such as a feverish child, or a child who appears weak, or has an immune deficiency that also require medical interventions.
Treating and Preventing Dry Cough in Adults
Avoiding a dry cough entails care to common triggers which include; viruses and environmental factors. Adherence to good hygiene by regular hand washing may prevent viral infections. Inhalation of second hand smoke and exposure to pollen, dust or any other allergens that trigger dry coughs should be avoided as well.
Further, using a humidifier within dry environments, and proper sanitary measures within the child’s compound have been known to prevent dry coughs.
Ways Of Preventing Wet Cough In Children
The focus does not only seem to be on wet cough but rather lung infection altogether and in most cases, appropriate prevention measures are considered. Particularly, frequent washing of hands and avoiding contacts with people down with infections such as bronchitis or pneumonia can reduce infections.
Making sure the child is vaccinated also including the flu jab is helpful in warding off diseases responsible for causing the wet cough. Otherwise, a healthy diet, adequate water intake, and rest all work in aiding the immune system and subsequently, preventing wet coughs.
Conclusion
There is much difference between understanding what a dry cough is and what a wet cough is, so proper treatment and care can be given with this information correctly at hand. The common cause of dry cough cases can be viral infections or an irritant in the environment but for wet coughs the cause is infections that produce mucus.
A last resort caller pharmacy treatments and other prescription drugs can be combined with a few homely remedies to tackle either case. Parents should attempt to record the time and intensity of coughing episodes in their child to take to their physician if necessary. People who are educated can keep their child safe and ease any cough related sickness with ease.
FAQs on Coughs in Children
Q: What are the possible causes of dry cough in children?
A: Most cases of dry coughing in children can be attributed to viral infections, particularly the common cold or influenza. Environmental factors such as smoke and medical conditions like asthma and allergies can also trigger dry coughs.
Q: How many days will a child cough in case of a wet cough?
A: A wet cough can last between 1-3 weeks, depending on the underlying cause. If the cough stems from a respiratory infection, it may take time to resolve. Consult a doctor if the cough becomes excessive or prolonged.
Q: What’s the best home remedy for dry cough?
A: Dry cough can be relieved by consuming warm liquids, using honey (for children over one year), and using humidifiers. It’s crucial to monitor the cough and seek medical attention if it worsens.
Q: Is it possible for a wet cough to worsen?
A: Yes, a wet cough can worsen if not treated properly, potentially leading to pneumonia or bronchitis. If the cough persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, it’s important to see a doctor.
Q: How long should a child’s cough last before I take them to a doctor?
A: Consult a physician if a child’s cough lasts more than two weeks, especially if it’s accompanied by a high fever, blood-streaked sputum, or breathing difficulties.

Russell F. Jones, holding a Master in psychology from the University of Florida. He writes for Smart Parent Solutions, offering practical advice on parenting and child development. His engaging content helps parents navigate family life with confidence and ease. Russell enjoys sharing his knowledge and spending quality time with his family.
