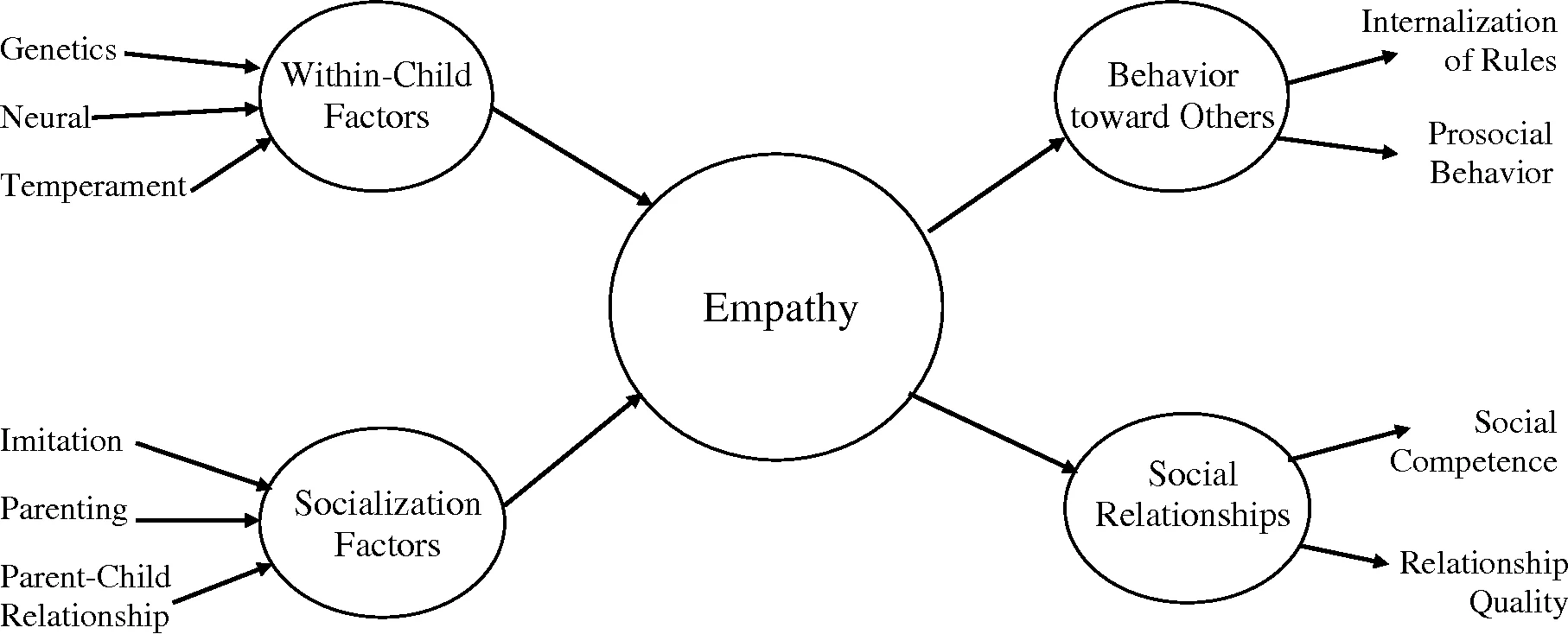
Empathy is the capacity of an individual to understand and share feelings with others. It is important in social relationships as well as daily interactions affecting personal relationships and professional collaborations too.
Childhood, which entails empathy development, goes through different phases until adulthood takes over. Knowing these stages can help us improve our cultivation of empathy thus leading to improved emotional intelligence and better interpersonal relationships.
empathy development stages
Empathic Concern in Infancy
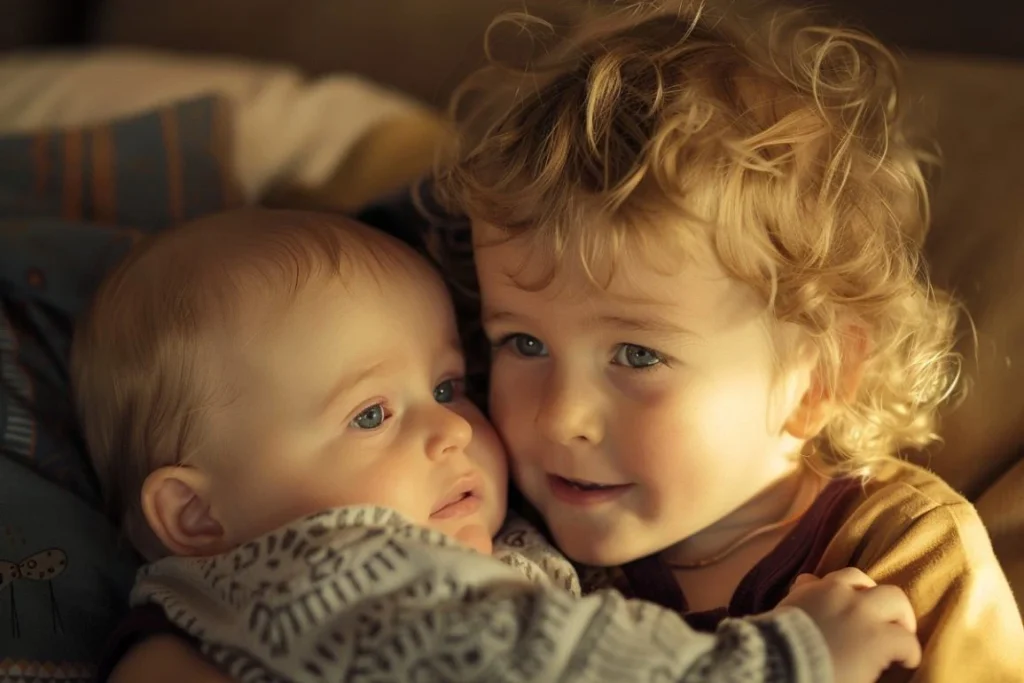

Initially called empathic concern, infants are able to identify and react to emotions expressed by others as the first stage of their empathy growth.
The phase generally lasts from birth up to the age of two.
Key Characteristics
| Copying Emotions | Infants frequently copy facial expressions and emotions demonstrated by caregivers. |
| Agony Response | Infants might cry when they hear other babies crying showing elementary forms of sympathy. |
| Bond Attachment | A bond of strong emotion between a child and his or her caregiver helps develop empathy. |
How to Develop Empathic Concern
| Responsive Caregiving | A parent or caregiver who responds to the needs of an infant very promptly helps him/her build up a sense of security and trust |
| Emotional Expression | Show the baby several emotions to make it able to recognize and comprehend different feelings. |
| Positive Reinforcement | Encourage them in gentle interaction with others including siblings or peers. |
Emotional Understanding in Early Childhood
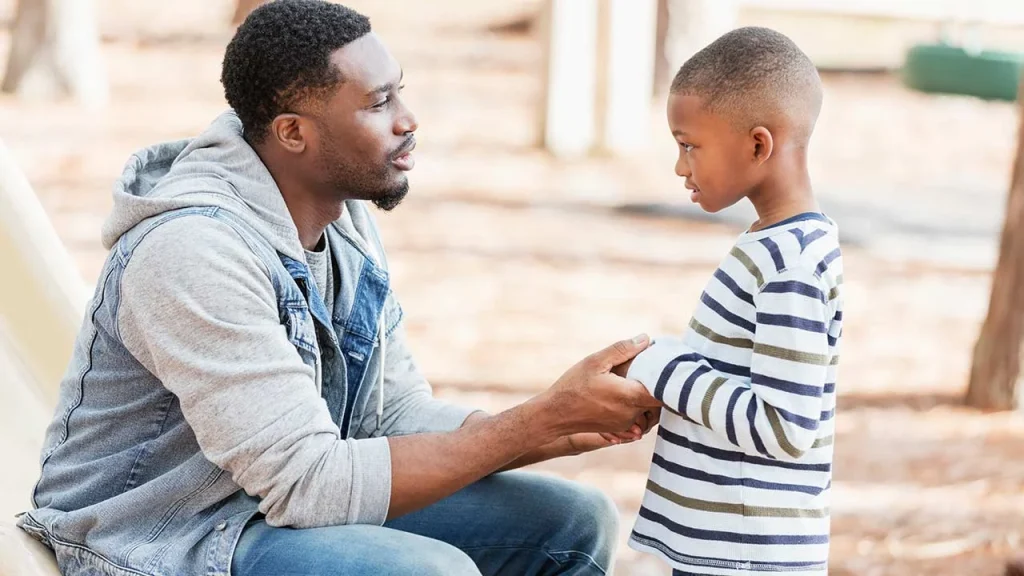

During early childhood, which usually takes place between ages 2 and 7, children start to become more aware than ever of emotions. They begin recognizing, naming such feelings in themselves as well as other people’s.
Key Characteristics
| Emotion Recognition | Children learn how to differentiate among various basic emotional states like joy, gloominess, anger or fright. |
| Language Development: | The use of words gives children an avenue through which they can express themselves better about what they feel inside. |
| Empathic Behavior | Concern for others’ welfare becomes apparent; when someone is unhappy, the child may try comforting them. |
How to Foster Emotional Understanding
| Emotion Coaching | Discuss emotions on regular basis and help children name their own feelings. |
| Storytelling | Use stories and books that emphasize diverse emotional situations as well as responses thereto. |
Expanding Perspective-Taking in Middle Childhood
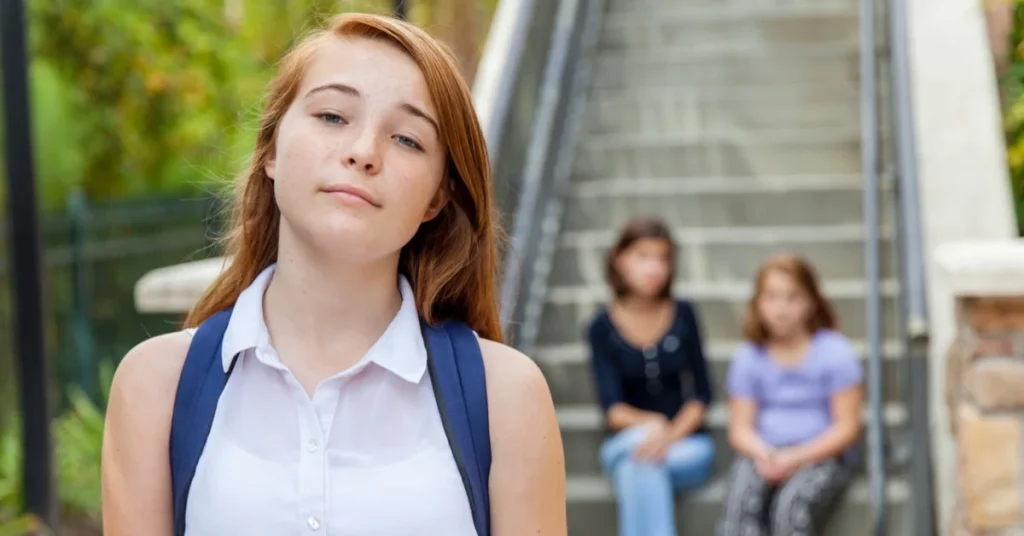

In middle childhood, between ages 7 and 12 typically, children develop the capability of adopting another’s point of view. This stage signals a substantial advancement in empathy development because of the comprehension that others may have different thoughts and feelings different from one’s own.
Key Characteristics
| Theory of Mind | Children understand that other people think differently, hold diverse beliefs and possess emotions. |
| Complex Emotions | Ability to comprehend complex emotions such as envy, remorse and honor. |
| Social Awareness | Better understanding of social cues and improved ability to navigate social situations. |
How to Enhance Perspective-Taking
| Discussion | Allow open discussions about how other may feel in particular cases. |
| Group Activities | Engaging children in group activities help them practice empathy and cooperation. |
| Conflict Resolution | Teach children techniques for conflict resolution to enable them resolve disputes empathetically. |
| Role-Playing | Get involved into role playing activities aimed at fostering empathy as well as understanding. |
Empathy In Adolescence
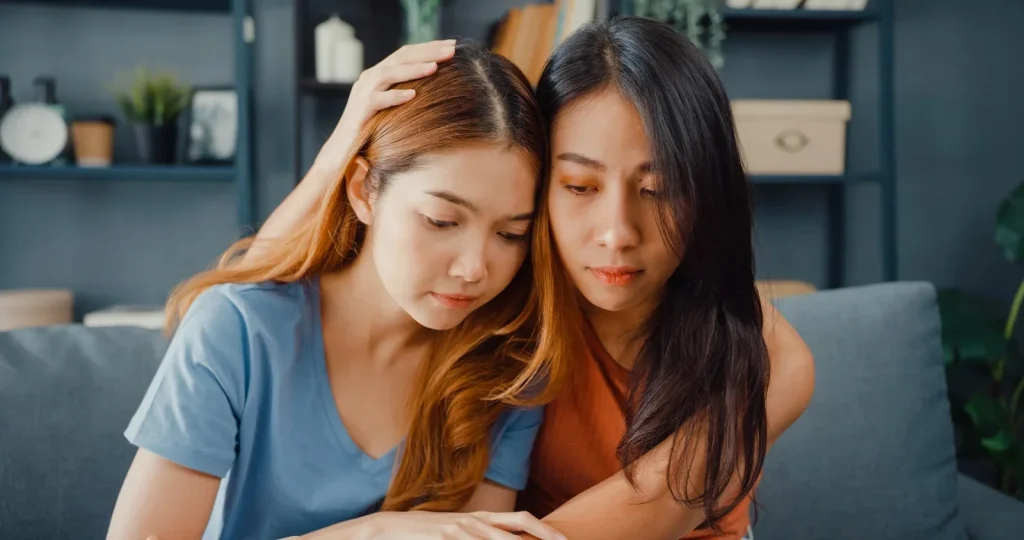

Adolescence which falls within the age bracket twelve through eighteen years is a crucial period for developing empathy. They fine-tune their understanding of complex emotions and relationships while expanding their social world widely.
Key Characteristics
| Abstract Thinking | Heightened capacity to think in abstract terms and view things from different angles at the same time. |
| Identity Formation | Developing a sense of self that involves recognizing their own values as well as those of others. |
| Moral Reasoning | Boosted ability to participate in moral reasoning and reflect on ethical dimensions of acts. |
How to Support Empathy in Adolescence
| Open Communication | Keep open channels of communication for discussing feelings and experiences. |
| Community Involvement | Promote community service or volunteer work to develop empathy through actions. |
| Model Empathy | Show empathetic behavior in your dealings with other people. |
Mature Empathy in Adulthood
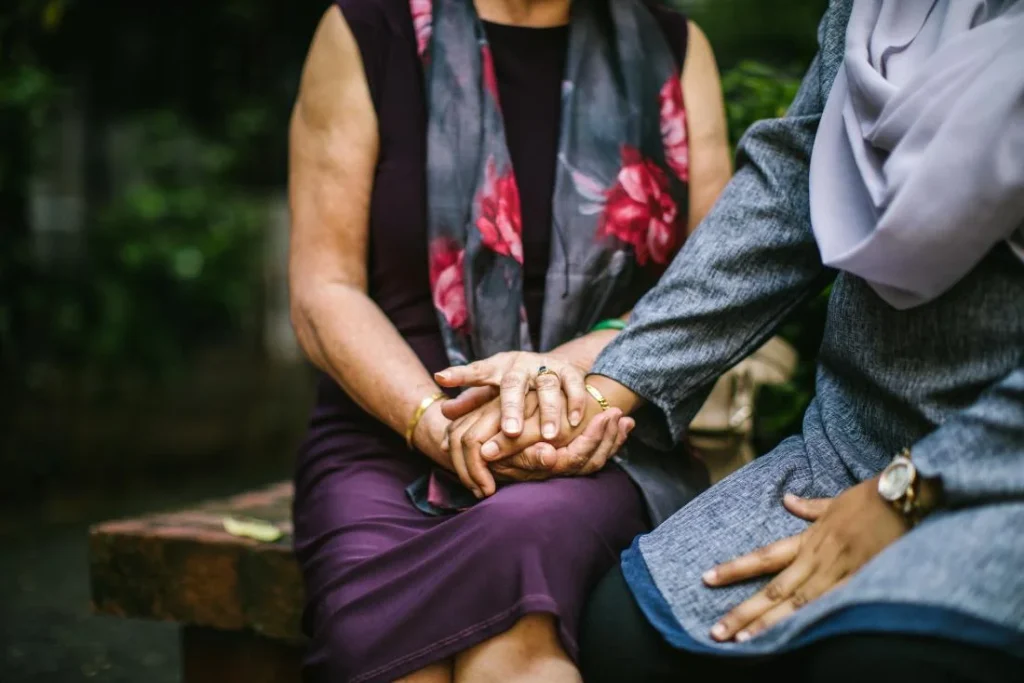

Mature empathy refers to a fully grown quality which enables a person to understand and react towards the emotions of someone else by integrating cognitive and emotional facets of empathy.
Key Characteristics
| Emotional Regulation | Adults can control their own feelings while at the same time showing empathy for others |
| Deep Relationships | It contributes to deeper, meaningful personal and professional relationships. |
| Global Perspective | A broader understanding about how culture influences emotions and behaviors. |
How to Foster Grown-Up Empathy
| Lifelong Learning | Continually learn about different cultures, perspectives and emotional intelligence. |
| Active Listening | Train yourself in active listening so that you can fully understand and react to others’ emotions. |
| Reflective Practice | Internalize every emotion you experience or interaction with others to make empathetic skills better. |
Tips for Boosting Empathy
Practical Approaches
| Becoming Conscious of the Present Moment | Cultivating mindfulness through meditation increases self-awareness and empathy. |
| Imaginative Sympathy | These exercises help in building empathy by making you imagine yourself as someone else entirely. |
| Empathic Feedback | Look for and offer empathetic feedbacks with an aim of learning and growing through it. |
Resources
| Textbooks | Empathy The Little Book Of” written by Roman Krznaric |
| Seminars | Participate in seminaries or workshops concentrating on emotional intellectuality and empathy skills. |
| Internet Classes | Enrol for online courses which train people on matters related to sympathy and emotional intelligence. |
Conclusion
Knowing the various developmental stages of empathy is very valuable in formulating emotional intelligence fostering meaningful relationships. By acknowledging and developing empathies throughout life’s stages we will have improved our abilities to connect with others thus creating a more humane world.
Whether you’re a parent, teacher or professional implementing these measures can make an immense difference on your capacity for feeling compassionately towards others as well as interacting kindly with them.
FAQs About Empathy Development stages
What are some of the advantages of nurturing empathy?
Having the feeling of empathy results into better associations, a deeper way of communicating and higher emotional intellect. It also makes society more compassionate and understanding.
How can parents teach their children to empathize?
Parents should be good examples when it comes to being empathetic, they should create a platform for discussion about feelings and emotions and finally encourage empathy building activities in the family unit.
Can anyone learn to be empathic?
Certainly! Empathy is something that can be learned or developed by using methods such as active listening, perspective taking exercises, emotional coaching.
Why is it important for employers to cultivate empathy at work?
Empathy at work promotes teamwork; it improves leadership and creates a positive work environment. It also assists co-workers in appreciating each other’s viewpoints so as to resolve conflicts amica.

Russell F. Jones, holding a Master in psychology from the University of Florida. He writes for Smart Parent Solutions, offering practical advice on parenting and child development. His engaging content helps parents navigate family life with confidence and ease. Russell enjoys sharing his knowledge and spending quality time with his family.