The circulatory system or cardiovascular system is very efficient, but it can be affected by many problems and illnesses, such as mitral valve prolapse, which may disturb its normal operation and damage the whole body. It is important to know about these diseases to detect, treat and prevent them early enough.
Diagnosis of High Blood Pressure in Circulatory System
Measurement of Blood Pressure

Mostly readings of blood pressure are used in diagnosing hypertension . A sphygmomanometer is used to measure this, giving two figures; systolic and diastolic pressure. Systolic is the one taken when the heart beats while diastolic represents that taken while the heart rests between two beats. The normal range for BP is usually below 120/80 mmHg.
Categorization
Blood pressure levels determine different stages of high blood pressure. They are as follows:
- Normal: Below 120/80 mmHg
- Elevated: Systolic between 120-129 mmHg and diastolic less than 80 mmHg
Assessment for Secondary Causes
Sometimes secondary causes may be responsible for hypertension such as kidney diseases, hormonal disorders like Cushing’s syndrome or obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Therefore further investigations should be done to detect these root problems which will in turn guide appropriate therapy
Treatment for High Blood Pressure
Lifestyle Changes
In most cases, doctors recommend adopting lifestyle changes as the first-line treatment against high blood pressure in circulatory system. These may include:
Dietary changes: Eating more fruits, vegetables, whole grains and lean proteins while limiting sodium intake as well as saturated fats and added sugars.
- Weight management: Striving for a healthy weight through a combination of dieting and exercising.
- Physical activity: Doing aerobic exercises such as brisk walking or jogging for at least half an hour every day.
- Smoking cessation: Stopping smoking can reduce significantly the chances of getting heart diseases related with hypertension.
- Limiting alcohol consumption: Women should drink not more than one standard drink per day whereas men should stick to two standard drinks maximum in any given 24-hour period.
Drugs
When lifestyle modifications alone fail to control hypertension, medications may be necessary. The following are some examples of commonly used antihypertensive drug classes:
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs)
- Calcium channel blockers
- Diuretics
- Beta-blockers
Which medication(s) to use is determined by various factors including the individual’s level of blood pressure, age, presence of other illnesses and side-effects susceptibility toward drugs
Regular Monitoring
Once treatment is started, regular monitoring of blood pressure is necessary to evaluate the efficiency of treatment in circulatory system and make modifications if required. This could mean going for check-ups with doctors from time to time or self-monitoring at home using a machine for measuring blood pressure.
Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis
Medical History and Physical Examination

A full medical history evaluation and physical examination usually marks the beginning of the diagnosis process. The healthcare provider will ask about things like smoking, high cholesterol, high blood pressure (hypertension), diabetes among other risk factors as well as symptoms such as chest pains or shortness of breath.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests may be done in order to see the arteries and detect plaque buildup; some examples include ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or angiography. These tests help in determining how much atherosclerosis has occurred and where it is located as well as identifying any blockages or narrowing within them.
Blood Tests
Cholesterol levels including, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and triglycerides can be measured using blood tests. It should be noted that atherosclerosis is associated with increased levels of low density lipoproteins also known as bad cholesterol.
Treatment for Atherosclerosis
Changes in Lifestyle
There are several ways through which atherosclerosisin circulatory system can be managed some of which include:
• Healthy Eating: This encompasses the consumption of fruits, vegetables whole grains lean proteins and limiting saturated fats trans-fats cholesterol sodium.
• Physical Activity: Individuals should engage in regular exercises like fast walking swimming cycling among others which are helpful in enhancing cardiovascular fitness hence keeping weight at bay.
• Quitting Smoking: This is important because it not only triggers atheroma but also other heart diseases.
• Stress Control: One may want to consider such stress relieving techniques as meditation yoga deep breathing exercises etc., for this will result into lower arterial pressures with enhanced personal wellness feelings being achieved.
Drugs
Atherosclerosis in circulatory system can be treated with drugs which manage risk factors and slow its progression. These may include:
- Statins: Commonly used statin drugs lower LDL cholesterol levels, thus reducing the possibility of cardiovascular events.
- Blood Pressure Medications: Medicines for controlling high blood pressure like ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers or calcium channel blockers can be prescribed to relieve the arteries from pressure and decrease risks.
- Antiplatelet Agents: They are drugs such as aspirin or clopidogrel that should be taken to prevent clot formation in blood vessels so as lessen chances of heart attack or stroke.
Medical operations
Sometimes surgeries are necessary when dealing with severe atherosclerosis or complications related to it such as CAD (coronary artery disease). Some of these procedures include:
- Angioplasty and Stenting: This is done by using a catheter that has got a balloon at its tip which is inserted into narrowed or blocked arteries hence widening them; moreover, stents are placed there to keep them open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): It involves going round obstructed coronary vessels using grafts taken from other parts of one’s body so that more blood can reach the heart muscle freely.
Diagnosis of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Review of Medical Records and Physical Examination
Typically, a thorough study of a patient’s medical record along with physical examination is carried out to diagnose CAD in circulatory system . In this case, they look out for symptoms such as angina (chest pain), shortness of breath, fatigue and palpitations.
Diagnosis tests
Different diagnostic tests can be used to validate the presence and measure the severity of CAD in circulatory system:
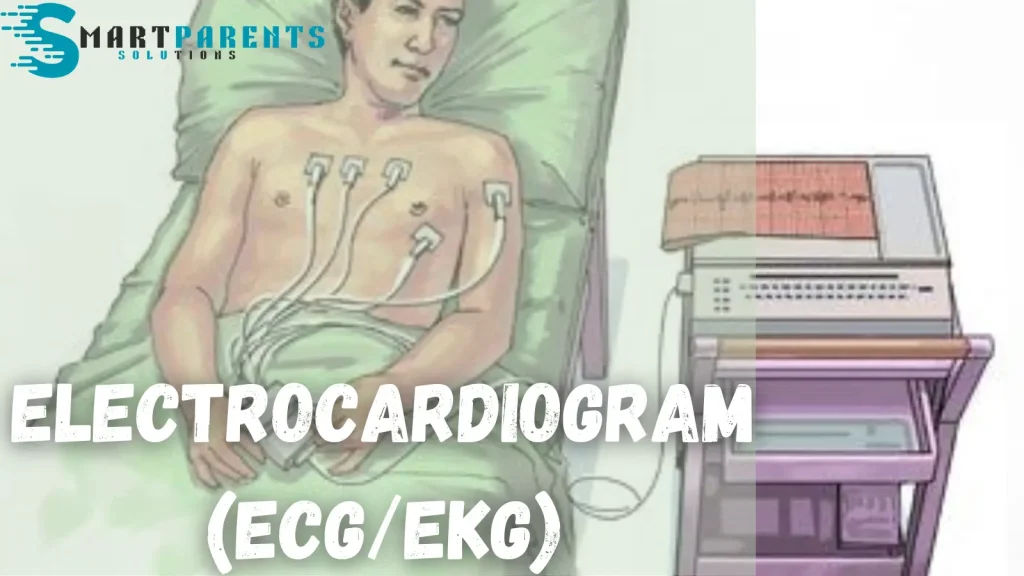
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG): This records electrical activity produced by your heart that could indicate ischemia or damage in the past.
- Stress Tests: Exercise stress tests can be done where you are asked to exercise more while pharmacologic stress test involves injecting drugs which make your heart work harder; these help to identify areas where blood flow may reduce.
- Echocardiography: It uses sound waves that bounce off different parts of the heart showing its structure, function and any defects present.
- Coronary Angiography: A special dye is injected into your bloodstream through a catheter inserted into one or both major arteries in the groin area up towards where they divide near either side of your waistline then X-ray images are taken as this dye moves through these vessels so that blockages can be seen clearly.
1.3 Imaging Studies
Advanced imaging techniques such as CT angiography or cardiac MRI may be used to assess coronary artery anatomy, blood flow, and cardiac function.
Treatment of Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
Modify the Lifestyle
To control and slow down the advancement of CAD in circulatory system, it is important to make some healthy changes in life:
• Dietary Modifications: This means eating food that is good for your heart which should be low in saturated fats, cholesterol and sodium, and high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains etc.
• Regular Exercise: Physical activities done frequently can enhance circulatory system well-being leading to lower blood pressure levels as well as a reduction in cholesterol levels.
• Smoking cessation: Stopping smoking plays a great role in preventing CAD itself along with its complications too.
2.2 Medications
A number of drugs may be given for the management of CAD in circulatory system or its risk factors such as:
- Antiplatelet agents: Aspirin or other antiplatelet medicines can help prevent blood clots from forming within the arteries.
- Statins: These are drugs used to lower cholesterol levels thereby decreasing the chances of having plaques built up in one’s arterial walls.
Invasive Treatments
When lifestyle changes and medications do not suffice, invasive treatments may be required:
- Angioplasty and stenting: These are minimal procedures that open blocked or narrowed coronary arteries with balloon catheters, and place a tube called a ‘stent’ to keep the blood vessel open.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): This surgery creates new paths for blood to flow by going around blocked heart arteries using blood vessels from other parts of one’s body.
Diagnosis of Heart Failure
Medical History and Physical Examination
Doctors will go through their patient’s medical background together with giving them a physical check-up so as to determine what symptoms they have been experiencing, signs – such as oedema or breathlessness – which indicate fluid retention in the body; also any other underlying conditions that might be causing these problems leading up into cardiac arrest.
Diagnostic Tests
In confirming the diagnosis and determining the severity of heart failure, diagnostic tests are very important. Among the tests which may be done include:
- Echocardiogram: This procedure produces detailed images of the heart’s structure and function to establish if there is any abnormality like weak muscles or valve problems.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): Records electrical activity in a person’s heart, helping identify either irregularities in their heartbeat rhythm or signs that they might have damaged their cardiac muscle.
- Blood tests: These measure biomarkers such as B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP). Elevated levels of these substances indicate a person is suffering from congestive heart failure.
- Chest X-ray: It helps determine how big someone’s heart is as well as its shape besides detecting whether fluids have started accumulating inside lungs or not.
Classification and Staging
Usually, doctors classify heart failure depending on symptoms’ gravity and cardiac function impairment extent. Such systems used for categorizing this condition most frequently are New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional classification system plus American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) staging system.
Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure
Lifestyle Modification
Here are some lifestyle changes that you need to make to manage heart failure:
• Restricting sodium: It will lower fluid retention and reduce the burden on the heart.
• Limiting fluids: Watch your liquid intake so as not to overload with fluids which can make symptoms worse.
• Regular physical activity: Exercising supervised by someone else helps in improving the cardiovascular fitness as well as quality of life.
• Quitting smoking: This act alone reduces further harm caused by smoke on both cardiac muscles themselves and blood vessels all over the body.
• Weight control: Attaining a desirable range of weight for oneself then sticking within it takes away some load off functions of the heart.
2.2 Medicines
Drugs assist in managing symptoms, improving heart function and preventing complications associated with this condition in circulatory system. Commonly used medications for congestive cardiac failures are;
- ACE inhibitors/ ARBs; these drugs expand blood vessels thereby lowering BP but also increasing myocardial contractility (positive inotropic effect).
- Beta-blockers; they slow HR, decrease BP thus increasing ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF).
- Diuretics; these drugs help to eliminate excess water from the body system hence less fluid accumulates in the lungs or legs
Diagnosis of Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Reviewing Patient Records and Conducting a Physical Examination
It is important to check records to know about past illnesses or conditions that the patient may have had. In addition, the doctor will perform a thorough physical examination which involves looking for weak pulses, cold skin and leg ulcers.
Testing the Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
The ABI test checks blood pressure in the arms against that in the legs to establish how well they are flowing. If it is low then this means there is peripheral arterial disease whereby vessels get narrowed by atherosclerosis hence reducing blood supply.
Doppler Ultrasound
This method uses high-frequency sound waves to produce pictures of blood vessels showing whether they are narrowed or blocked.
Angiography
A special dye is injected into an artery during angiography followed by taking x-rays to find out where they might have become narrow due to plaque buildup as well as their severity levels.
Treatment for Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Changes in Lifestyle
Stop Smoking: Giving up smoking is the most important thing to do when treating PAD since it makes the disease progress much faster.
Exercise: Programs of supervised exercise such as walking may relieve claudication symptoms and increase walking distance.
Healthy Eating: Eating diets low in saturated fat, cholesterol and sodium can assist in controlling blood pressure thereby reducing cholesterol levels which are known to cause heart problems.
Drugs
Antiplatelet Agents: Doctors usually prescribe these drugs like Clopidogrel or Aspirin to prevent clotting and other events related to blood vessels blockage.
Statins: They are used so as to lower cholesterol levels thus slowing down plaque formation within arteries hence bringing about improvement in conditions associated with this ailment.
Blood Pressure Medicines: People with PAD must manage their high BP well if they want better outcomes.
Invasive Procedures
Angioplasty – a catheter with a balloon tip is inserted into the narrowed artery where it is inflated, thus widening the vessel. A stent might be put in place to keep the artery open
Bypass Surgery – this operation diverts blood flow around blocked or narrowed parts of an artery by using a graft when angioplasty fails or cannot be done.
Controlled Cardiac Rehabilitation
Full care programs for the heart offer complete support services to the patients having peripheral artery disease (PAD) such as exercise training, teaching risk management as well as counseling.
Amputation Prevention
To avoid amputation among individuals with severe tissue damage or critical limb ischemia, wound care must be given priority to promote healing through antibiotics and other necessary interventions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, good health and wellness require people to ensure that they are diagnosed and treated correctly in case of circulatory system disorders. Healthcare providers can easily circulatory system disorder if they employ sophisticated diagnostic methods followed by personalized therapies designed towards each patient’s unique needs. The management involves lifestyle changes; drugs use control together with surgical operations where necessary hence these illnesses need early identification while providing individualized attention alongside education for self-care which helps them take charge over their own lives thereby improving quality living standards too.
Q. How can you know if you have Coronary Artery Disease?
A. To check for CAD, doctors may use an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG), stress tests, echocardiogram, coronary angiography and cardiac CT or MRI scans. These tests show how well your heart is working, if blood flows through it appropriately and whether there are any blockages in the arteries that supply the heart muscle.Q. What kinds of treatments are there for Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)?
A. Sometimes lifestyle changes such as dieting may be enough treatment to get BP under control; people should also exercise regularly and healthily lose weight where necessary; quit smoking where applicable while reducing stress levels too much; sometimes drugs like diuretics (water pills), beta blockers ACE inhibitors or calcium channel blockers might need to be given to bring down readings when all these things have failed.Q. How is heart failure controlled?
A. The treatment for heart failure in circulatory system consists of medication, lifestyle changes and sometimes surgery. These drugs may include ACE inhibitors, beta blockers, diuretics and aldosterone antagonists. Lifestyle modifications may involve exercise restriction and dietary change in addition to fluid limitation. In some extreme cases, pacemakers could be implanted as well as defibrillators or left ventricular assist devices (LVADs). A person’s heart might also need to be transplanted.Q. What are the methods used in treating Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)?
A. Various treatments exist for PAD of circulatory system such as working out more often, quitting tobacco smoking and making necessary dietary adjustments. Antiplatelet agents could be taken together with statins while medications meant for BP control or controlling blood sugar levels can be prescribed where necessary too. Angioplasty may have to be done with stents or bypass surgery depending on the severity of the case so as to restore normal blood flow into affected limbs.
Russell F. Jones, holding a Master in psychology from the University of Florida. He writes for Smart Parent Solutions, offering practical advice on parenting and child development. His engaging content helps parents navigate family life with confidence and ease. Russell enjoys sharing his knowledge and spending quality time with his family.