Introduction
Ankyloglossia is often referred to as tongue-tie newborns and affects newborns and their families. This results from short, thick, or tight lingual frenulum in these infants which makes them unable to move their tongues properly.
Failure to be able to move the tongue can influence breastfeeding as well as language development. As a result, parents or guardians must understand its causes, symptoms, and what could be done about it. Thus, parents must get familiar with available treatments that can help manage the condition of a child having Ankyloglossia.
What is Tongue-Tie Newborn ?
Definition and Overview
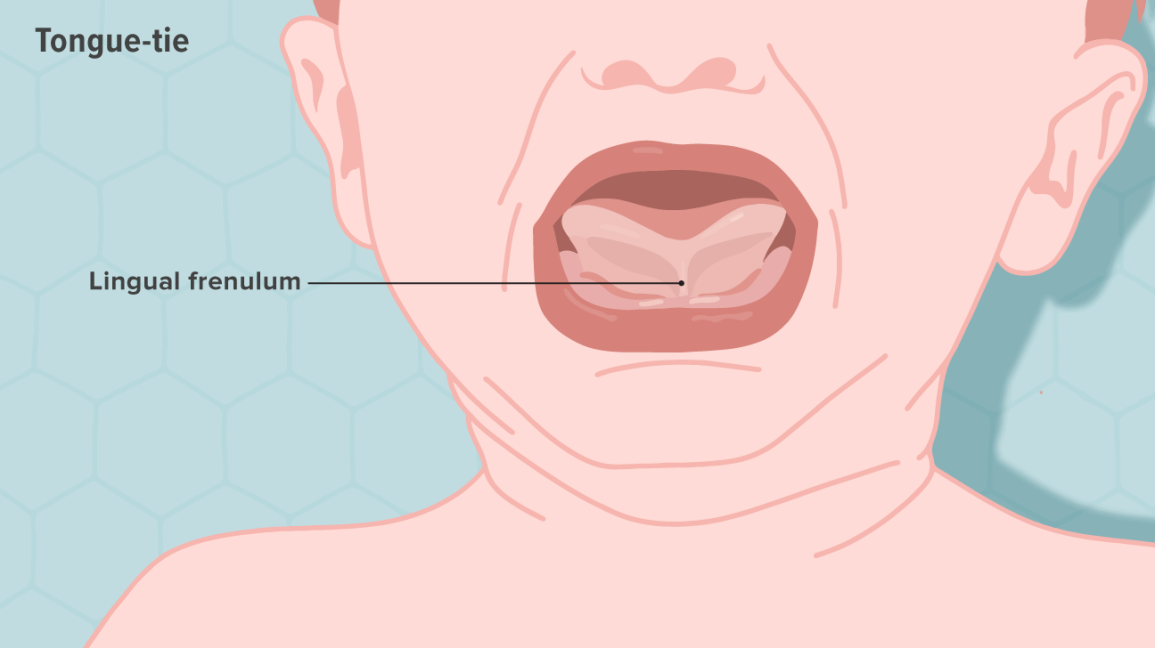
Tongue-tie Newborns, also called Ankyloglossia in medical terms, refers to a congenital condition where the lingual frenulum is abnormally short, thick, or tight; it connects the underside of the tongue to the floor of the mouth limiting the free movement of the tongue. Some cases involve restriction more than others but others are mild.
Tongue-tie may make breastfeeding challenging because infants cannot latch correctly. This condition may persist into a child’s speech and oral hygiene leading to late treatment calls for early attention.
How Prevalent is Tongue-Tie Among Newborns?
It is worth noting that there are many criteria used by health professionals thus causing variation in estimates of prevalence rates among newborns ranging from 4% – to 10%. However, most children with tongue-tie syndrome are boys; the reason is unclear.
According to some scientific research, however, this medical condition seems hereditary since it may be inherited through genes carried in a family tree. The necessity of an intervention depends on how severe the case under discussion is. For example, mild cases may not cause any problems while others need to be corrected.
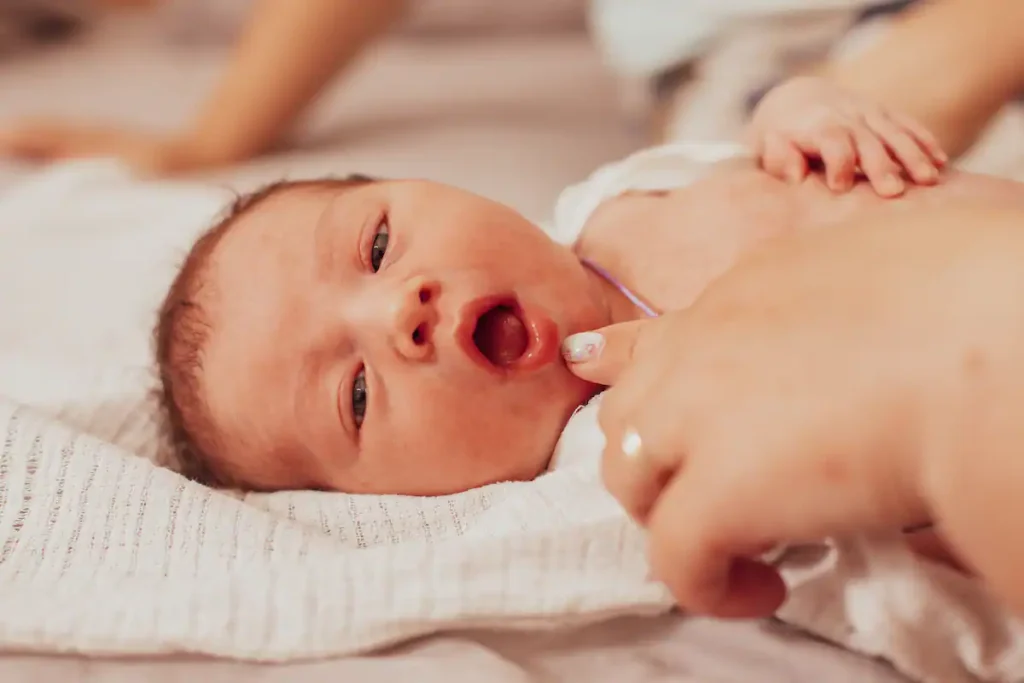

Symptoms and Signs of Newborn Tongue Tie
Identifying tongue tie in newborns
New parents, who have no idea about this condition, may find it difficult to detect tongue-tie in their newborns. However, various telling signs can be observed. For instance, the first symptoms include breastfeeding difficulty.
The infant might experience challenges latching onto his/her mother’s breast properly resulting in insufficient milk intake and poor weight gain which may lead to malnutrition in babies.
The mother could also undergo pain during feeding like sore nipples together with frequent mastitis incidents due to improper positioning or latch-on technique by her baby.
Other Manifestations and Symptoms
There may be many other ways in which infants with feeding problems manifest tongue-tie. Speech disorders can emerge during childhood as a result of limited tongue mobility, making some sounds difficult to pronounce. This situation brings about frustration as well as delays in learning how to speak by children.
Misaligned teeth are also a possibility due to the constrained movement of the tongue that affects oral development leading to gaps between lower anterior teeth. Oral care is compromised because food particles remaining on teeth and gums cannot be effectively cleaned off by restricted tongue movement, hence increasing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
What Can Cause Newborn Tongue Tie?
The main cause of tongue tie in Newborns is still being researched but it is generally believed to be present at birth or congenital. Normally, the lingual frenulum separates from the floor of the mouth allowing free movement of the tongue during fetal development.
However, there are instances where this separation does not take place completely leading to a condition called tongue-tie. It has been suggested that genetics could play a part since this disorder often runs in families.
The exact inheritance patterns have not been fully elucidated; however, babies born into families wherein either parent had undergone surgical treatment for ankyloglossia or similar afflictions are more likely to develop the disease themselves.
Factors that Increase the Risk of Tongue-Tie in Newborns
Tongue tie in Newborns is influenced by some factors. One such factor is the family history of a patient which may indicate a possible genetic inheritance. Other risk factors include gender which affects boys more than girls.
Furthermore, other congenital disorders like Pierre Robin sequence and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome increase the chances of an individual being tongue-tied at birth. Additionally, certain things happen during pregnancy for example; if a woman has diabetes, then this will heighten the risks of having her child’s tongue though these assertions remain weak based on inadequate research.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
How is Tongue-Tie Diagnosed in Newborns?
Health professionals often perform physical examinations immediately after birth to determine whether a baby has tongue-tie Newborns. The physician checks how the baby’s frenulum looks and moves as well as any restrictions or abnormalities thereof.
Various instruments and ways can be employed to establish how severe tongue-tie newborns are such as the Hazelbaker Assessment Tool for Lingual Frenulum Function which measures tongue lift, spread, and frenulum elasticity among other criteria.
Feeding problems are usually the first signs observed by parents who seek further medical advice from their pediatricians. Thus early diagnosis should be made to initiate timely interventions leading to improved feeding practices while preventing future complications.
Tests and Assessments for Ankyloglossia
Apart from physical examination, other evaluations may be required to ascertain the extent of Newborn tongue tie. For babies having difficulties with breastfeeding, a lactation consultant can carry out a detailed assessment and provide advice.
These professionals are good at identifying problems related to latching on and could suggest some techniques or interventions that could be useful in those cases. In addition, speech pathologists can carry out assessments to determine articulation disorders and other aspects relating to speech for older children who may have language issues.
Treatment Options for Tongue-Tie
Non-Surgical Treatments
For minor cases of tongue-tie, non-surgical treatments might work best as these often use different approaches concomitantly. Since proper breastfeeding skills can alleviate many challenges, lactation support is generally considered the first option for this purpose .
It’s important to work with a lactation consultant so that both mother and child achieve better latch-on and more efficient feeding. Speech therapy is another approach that can be employed particularly when dealing with older children who experience problems such as delayed speech development or difficulties talking at all.
SURGICAL OPTIONS (FRENOTOMY AND FRENULOPLASTY)
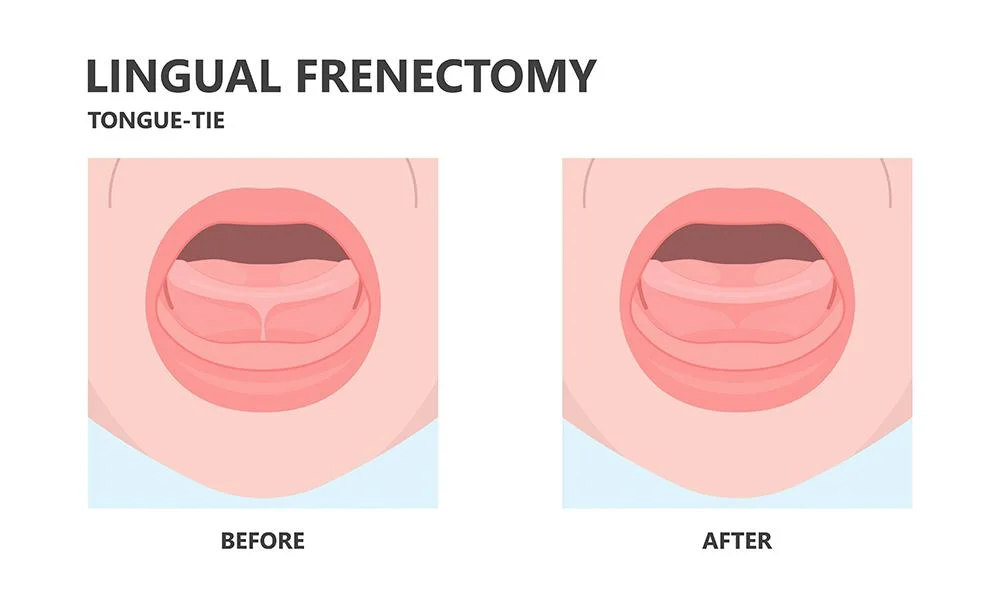
In more serious cases, surgery may be necessary to free the tongue and enhance proper movement. The two most prevalent surgical alternatives are frenotomy and frenuloplasty. Frenotomy is a minor procedure that simply requires cutting of the frenulum; thereby enhancing movement of the tongue.
This procedure can often be done at the doctor’s office with moderate discomfort and recovery time. By contrast, Frenuloplasty is an extensive procedure that could require suturing along with more protracted recuperation periods.
Typically, this option is meant for more complicated cases or older children where a mere frenotomy may not suffice.
WHEN IS SURGERY RECOMMENDED?
Occasionally, a severe Kind of tongue-tie Newborn that does not allow speech, feeding, or oral hygiene adequately may call for surgery. Therefore, considering its potential advantages and disadvantages, parents should decide on whether or not they have to undertake an operation.
Some factors that might influence this include how bad your condition is, how old your child is, and whether there are any other symptoms related to this or complications resulting from this disease.
For babies who are struggling with feeding, prompt surgical intervention can prevent malnutrition deficiencies while enhancing breastfeeding success rates. To heighten communication skills and enhance self-confidence, speech problems can be treated surgically in older children.
Living with Tongue-Tie Newborns
Effects on Breastfeeding and Bottle Feeding
At the earliest stage of life when feeding is vital for growth and development, living with tongue-tie Newborns can throw up different challenges. Particularly, breastfeeding tends to be an uphill task because it may make an infant not latch appropriately thereby leading to inefficient milk transfer and poor weight gain.
Forcing the baby to suckle under such conditions leads to suffering from pain and frustration by both the baby and mother. On the other hand, bottle feeding has its fair share of challenges since some babies may still fail to form an adequate seal around their nipples.
Advice for Parents and Caregivers
Parents as well as caregivers of children suffering from tongue-tie can manage this condition through some strategies hence improving their lives’ quality. It is important to seek professional help; lactation consultants, pediatricians, or speech therapists have great experience working with children who have this condition.
As a parent monitoring your child’s growth process will enable you to monitor eating trends that keep your baby healthy enough. Parents should also be patient and persistent because it takes time and effort to overcome problems caused by tongue-tie Newborn.
Using special feeding tools and performing gentle stretching exercises can also work well in enhancing the symptoms and improving the feeding outcomes.
Prevention and Outlook
Can Tongue-Tie Newborns Be Prevented?
At present, there is no known method of preventing tongue-tie which is a congenital condition existing from birth. Nevertheless, recognizing the issue at an early stage as well as being aware of it are vital factors that contribute towards managing the condition effectively.
Parents who have a family history of tongue-tie Newborns or related conditions should be particularly vigilant in case of suspected cases. Though prevention may not come out straightforwardly, timely intervention can help to reduce the impact of this condition on feeding and speech development.
There is ongoing research investigating genetic and environmental aspects contributing to tongue-tie to develop preventive strategies in the future.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
In general, prognosis for children with tongue-tie is good especially when the problem is identified and managed early enough. There are significant improvements in feeding abilities as well as speech among many children following appropriate interventions.
In some instances, without any need for medical treatment, a frenulum may stretch spontaneously until resolved.Still, regular monitoring and follow-up are necessary, especially to check for speaking ability and dental growth. Parents should be vigilant of any relapses or complications.
The majority of children with tongue-tie Newborn can have normal lives without sustained adverse effects if managed appropriately.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Signs You Should Seek Medical Advice
If you suspect your baby has a tongue-tie, you must get in touch with an appropriate healthcare provider as soon as possible. Numerous signs call for medical evaluation like persistent breastfeeding difficulties or problems with bottle feeding, the mother experiencing recurrent pain during feeding, and poor weight gain by the child.
Language delays or disorders may mean pediatricians look towards early interventionism for ideal upbringing. Besides, dental issues such as tooth gaps or other oral anomalies also need expert opinions on them. Seeking timely advice from the pediatrician, lactation consultant, or other specialists will clarify things and help direct appropriate treatments.

How to Get Ready for Your Appointment
Getting ready for a healthcare appointment can help maximize your time with the provider; keeping in mind that it is essential to evaluate the benefits of any possible procedure about the risks.
The information will be useful to a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and recommended interventions. In addition, make a list of queries or concerns about tongue-tie and how it should be managed.
Again, having another adult like a partner or family member alongside can help support you more and also help in recalling important things discussed during that visit.
Conclusion
Various difficulties may result from tongue-tie in newborns ranging from problems associated with feeding to those relating to speech as well as dental matters. However, understanding, timely intervention, and early recognition of this condition can go a long way toward managing most of these issues effectively.
Despite its commonality, this ailment should not shape the formative years of your child’s life. Parents can ensure that their children receive appropriate treatment by discussing with healthcare professionals and adhering to prescribed intervention regimes.
Children with tongue-tie can recover normal growth patterns and development when given necessary assistance.
FAQs
Is tongue-tie a serious condition?
What is true of this disorder is that it can present in varying degrees, ranging from mild to severe and may not be life-threatening but could affect feeding, speaking and even oral hygiene and early intervention can help control some of these issues.
Can tongue-tie correct itself over time?
In other cases, the frenulum might naturally stretch or loosen as the child becomes older. However, this is not guaranteed because there are instances where medical intervention will be required.
Is tongue-tie surgery painful for infants?
Frenotomy, which is the most commonly performed method of removing an abnormal frenulum, is typically a brief process that involves minimal discomfort to the child. There are various methods of handling pain that make certain that babies find themselves at ease.
Can tongue-tie cause speech problems?
Yes: constrained tongue movement due to tongue-tie Newborns may affect speech hence it needs to be checked out immediately for any possibility of pronunciation problems.
If I think my baby may have a tongue-tie Newborn, what should I do?
When you believe that your child has a tied tongue, it is good to see a doctor who will perform a comprehensive examination of the situation and will get consultations with pediatricians and lactation consultants as well.
The video content featured on this website is credited to the YouTube channel “Doctor O’Donovan” All rights and ownership of the video belong to the respective creators at “Doctor O’Donovan.” We do not claim any ownership of the video and are sharing it solely for informational and educational purposes. Please visit the “Doctor O’Donovan” YouTube channel for more content and subscribe to support their work.

Russell F. Jones, holding a Master in psychology from the University of Florida. He writes for Smart Parent Solutions, offering practical advice on parenting and child development. His engaging content helps parents navigate family life with confidence and ease. Russell enjoys sharing his knowledge and spending quality time with his family.