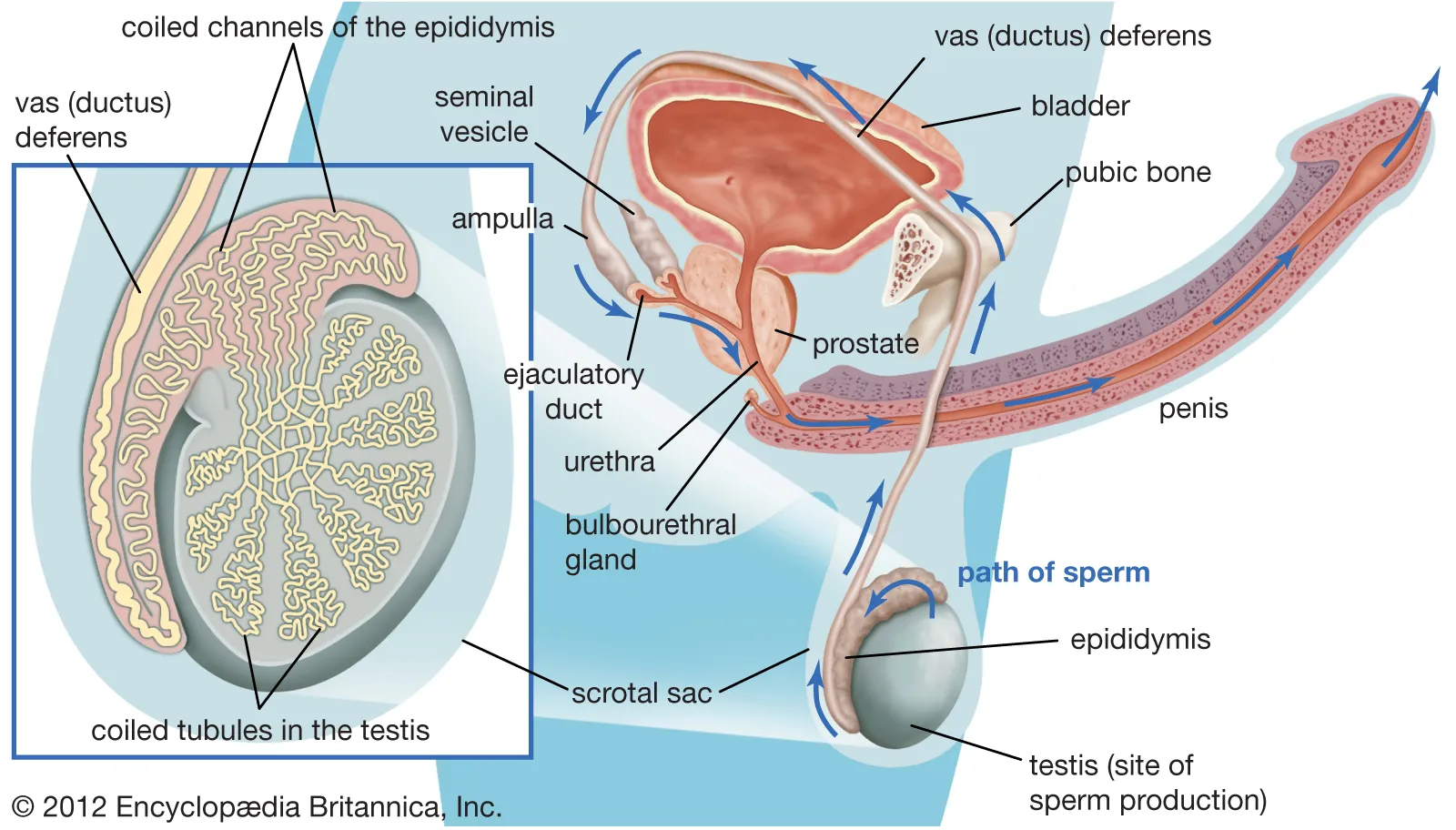
I am guide about the male anatomy, especially the male reproductive system like the penises and testicles. The penis works as a copulatory organ and also serves as male waste excretory organ. It has three main parts which are; root, body and glans penis.
Penis Structure
Root: Base of the penis which is located internally and it supports it by attaching it to the pubic bone.
Body (Shaft): An erectile tissue that makes up this cylindrical portion of the penis that is responsible for erection during sexual arousal.
Glans Penis: This round tip on a penis contains full of nerve endings giving more pleasure in sexual intercourse.
Erectile Tissue
There are two kinds of erectile tissues found in the penis:
Corpora Cavernosa: Two parallel chambers running along the topside of the penis responsible largely for maintaining its stiffness while erect.
Corpus Spongiosum: A single chamber surrounding urethra ensuring that when ejaculating there would be no blockage.
Blood Supply and Erection
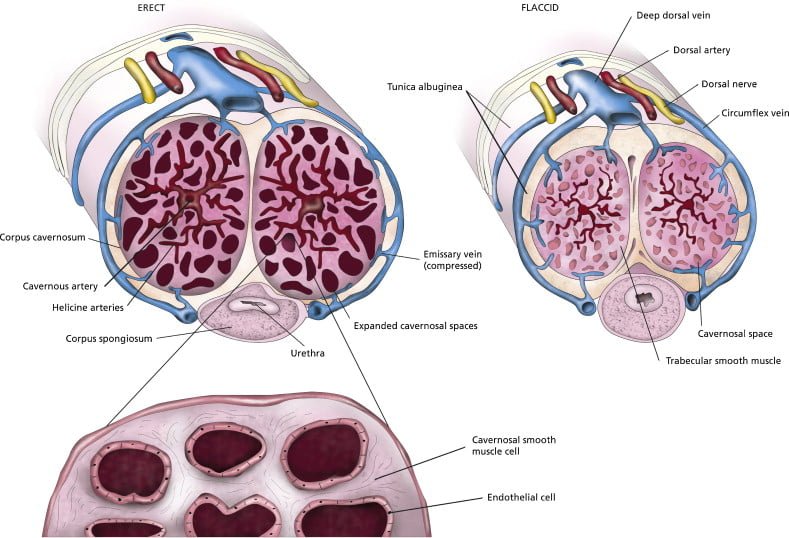
The presence of blood in the erectile tissue fills up the penis leading to its erection. This is prompted by a reduction of the tension in smooth muscles of the penis that assists in filling erectile chambers with blood.
Testes
Sperms production and synthesis of testosterone hormone, which happens to be main hormone for males are functions done by testes also referred to as male gonads.
Testes Structure
It is a scrotum; it is a pocket outside that houses two testicles and provides an ideal temperature for sperms production.
Tissues in the Testis
It has scrotum that contains seminiferous tubules which produce spermatozoa and interstitial cells or Leydig’s cells which generate testosterone hormone.
Spermatogenesis
Mitotic division, meiosis as well as spermiogenesis end up with formation of mature sperms capable of fertilizing ova produced by females.
Hormonal Regulation
The primary site of synthesis of testosterone is Leydig cell. It controls secondary sexual characteristics like development of facial hair and deepening of voice; besides maintaining libido and functioning during erection.
Reproductive Physiology: Erection and Ejaculation
The act of erection and ejaculation are parts that make up the major part of the male sexual response cycle controlled by intricate physiological mechanisms.
Ejaculation
For this reason, erection and ejaculation form most significant parts within male’s sex response cycle which involves complex processes carried out physiologically.
Erection
Sexual stimulation leads to erection beginning from sensory or mental stimuli. Nitric oxide (NO) neurotransmitters act on penile arteries causing smooth muscle relaxation thereby increasing blood supply into cavernous tissue.
Conclusion
Finally, comprehending male anatomy is necessary for maintaining productive health and addressing issues regarding sexual function. This article gives a detailed explanation of intricate structures, and physiological processes, you must be well conversant with all the information given to make any decision related to your sex life. In case you have any concerns or questions it’s always advisable to seek assistance from a healthcare provider.
FAQs on Understanding Male Anatomy
1. Which Parts of the Penis are Most Important?
The main portions of a penis include: root (situated inside and connected to pubic bone), body or shaft (enables it to become erect in response to sexual stimulation) and glans penis (a round head full of nerve endings for more pleasure during intercourse).
2. What is Erectile Tissue? Give Two Types.
These tissues are corpora cavernosa (two cavities maintaining rigidity throughout erections) and corpus spongiosum (which covers urethra from blockage during ejaculation).
3. How does Blood Supply Result in Erection?
Erection occurs as blood fills these tissues. When nitric oxide and other neurotransmitters induce smooth muscle relaxation, increased blood flow in the cavernous tissue facilitates erection.
4. What are the Functions of Testes in Males?
Male gonads or simply testes produce sperms and secrete hormone testosterone that is important for male reproductive as well as secondary sexual characteristics such as beard growth.
5. Define Spermatogenesis?
Spermatogenesis is when the seminiferous tubules inside the testes produce sperm by dividing mitotically, meiotic division then the complete transformation of spermatozoa capable fertilizing ovum.
6. Where do Testosterone Hormones Synthesized and What are its Roles?
Leydig cells within testicles mainly synthesize testosterone hormone which controls secondary sexual traits like growing of hairs on face especially beard, voice deepening while at the same time maintaining sex drive consequently erection.
7. How does one Control Erection and Ejaculation?
The male sexual response involves processes of erection and ejaculation regulated through complex physiological mechanisms involving stimuli like sensory or mental stimulant substances, neurotransmitters such as nitric oxide as well as smooth muscle relaxation.
8. Why is it Crucial to Comprehend the Male Anatomy?
Knowing the male anatomy helps to maintain reproductive health and deal with sexual function related problems. This will help you make informed choices about your sexual well-being.
9. Who Should I Approach for Specialized Advice on Male Reproductive Health?
When it comes to issues about male reproduction or any concerns regarding human sexuality, it is thus important that they seek advice from a healthcare provider who can help them come out of their fear.